Refrigeration
Overview
The broad area of refrigeration covers a large number of devices and applications including but most likely not limited to:
Refrigerators, freezers, cold rooms, temperature controlled transport, water coolers, milk chillers, and the production of separated industrial gases.
In the vast majority of cases, the process is run by a heat pump pulling heat out of the cooled space or substance. There are other processes such as Peltier Coolers but they are not in large scale use, and are not covered in this series of articles.
Refrigerators and Freezers
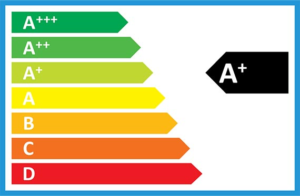
Refrigerators and freezers along with all “white goods” come with an energy rating.
Always remember that the purchase of such goods is a medium to long term investment, and that if an item is of a more efficient design, but costs a little more to buy, you will usually get back the additional investment in energy savings.
Also consider how long the standard warranty is as a product with a standard 5 or 10 year warranty is likely to have a longer design life and be constructed with higher grade more robust parts than one with a 1 or 2 year warranty. Long life products usually have lower embodied emissions per year of use than lower grade products as in the long run, less materials are used to replace worn out products.
Be sure to close the door, to keep the appliance defrosted, and to keep the condenser (coils on the back of the appliance) free from dust and debris so it can work efficiently. Wherever possible, locate in a cool shaded place, and not directly next to ovens, tumble drivers, or other appliances which get hot.
For help and advice Free Phone 0800 298 5424
Cold Rooms
In regards cold rooms, the kind of factors to look out for are:
Inverter controlled compressors and fans (Inverter / Variable Speed Drives run efficiently at all speeds)
Thicker or higher grade insulation
Quality door seals
Cold room strip curtains (to limit air flow in and out when going in and out)
The highest efficiency LED lighting possible minimising both direct electricity consumption, and the generation of heat in the cold room.
Larger condensers / heat exchangers and fans will generally be more efficient so long as the compressors (At least 2 to provide fail safe) are suitably sized.
Accurate digital temperature control with multiple temperature sensors throughout the cold room and data logging. (Data logging of cold room temperatures is a legal requirement for food hygiene).
Ideally you will locate the condenser / external unit in a cool shaded place on the North of the building if you have no use for the heat – however if you need hot water or space heating for offices, consider specifying the system to heat water with the heat removed from the cold room.
For larger cold rooms or refrigerated warehouses, consider gas engine heat pumps as the cost of gas per kWh is considerably less than electricity. (Gas engine heat pumps use an engine powered by mains gas rather than electricity to drive the compressor).
Water and Milk Chillers
Broadly similar principles apply to chilling water, milk, and food products in factories.
Industrial Gases
Liquid Oxygen, Liquid Nitrogen, Liquid air (Oxygen and Nitrogen together), CO2, and Argon are produced by chilling air to very low temperatures. The details of their production are beyond the scope of this article, however there is scope to operate these production facilities in a way that helps balance the grid – using power when available in excess at low cost – such as on a windy night in an area with lots of wind turbines, and switching off the process during peak hours. A good deal of heat is produced when making industrial gases which can be applied for space heating, water heating etc.
Liquid air technology is also being developed as an energy storage medium – producing liquid air when there is excess power available, and expanding it through a turbine during peak hours. This will ideally be hybridised with industrial processes giving off waste heat to warm the air on its way to the turbine, and refrigerated warehouses able to make use of cooling off the back of the process.
Why have an independent building survey?
Always have an independent building survey as this will highlight any property problems. Caveat emptor means ‘buyer beware’ and is why you need to have a building survey to find out if there are any problems within the property; the estate agent certainly will not advise you of any.
We feel that we have surveyed nearly every type of building, please phone us on Free Phone 0800 298 5424 and we will email an example survey of the type of property you are looking to buy.

We hope you have found this article useful
We hope you found the article of use and if you have any experiences that you feel should be added to this article that would benefit others, or you feel that some of the information that we have put is wrong, then please do not hesitate to contact us (we are only human). For more information contact us on Free Phone 0800 298 5424.
The contents of the website are for general information only and is not intended to be relied upon for specific or general decisions. Appropriate independent professional advice should be paid for before making such a decision.
All rights are reserved, the contents of the website are not to be reproduced or transmitted in any form in whole or part without the express written permission of www.1stAssociated.co.uk.

